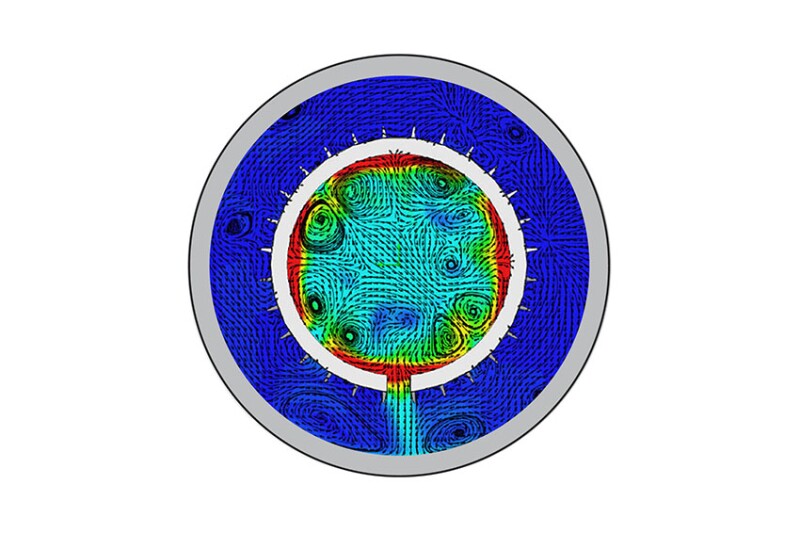
uring continuous injection, reservoir solids usually remain within the reservoir. However, prolonged or abrupt well shut ins can trigger intense transient flow phenomena like water hammer, backflow, and crossflow, causing fines and matrix sands to migrate and accumulate in the wellbore (SPE 187103). As a result, the accumulation of debris can markedly reduce structural integrity and the overall long-term viability of enhanced oil recovery (EOR) from the injection wells.
This issue had become particularly evident in an offshore field situated in the southern region of the Niger Delta. Over time, buildup in the well led to a substantial decrease in injection rates, which had significantly shortened the operational lifespan of the wells to just a few years at the anticipated injection rates. Various remediation technologies were attempted, such as tubing-installed valve and backflow-restrictor technology but both proved ineffective in resolving annular-flow and crossflow issues.
To prevent potentially expensive and complex interventions, sidetracking, or wellbore abandonment, further analyses by the operator, SNEPCo, concluded that an effective solution necessitated deployment as close to the sandface within the injector wells as possible.