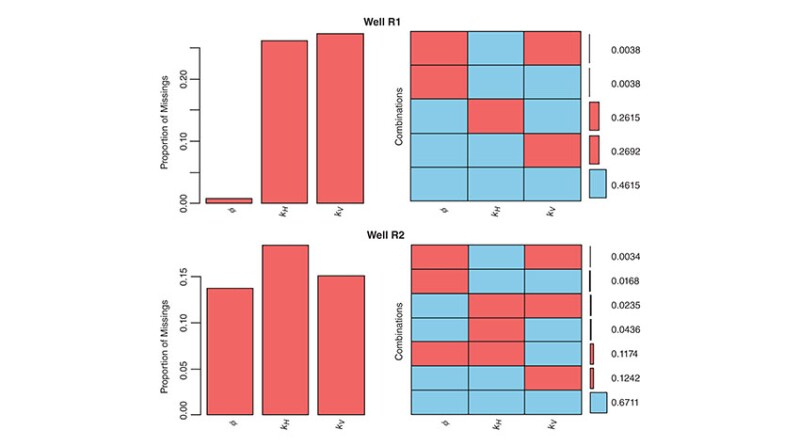
The study described in the complete paper comprehensively compares seven imputation techniques for predicting missing core-measured horizontal and vertical permeability and porosity data in two wells drilled in the North Rumaila oil field of southern Iraq. The results reveal that a data-imputation method consisting of multivariate imputation by chained equations (MICE) combined with classification and regression trees (CART) outperforms the other methods with the clastic and carbonate data sets studied. The novel workflow is suitable for application in both clastic and carbonate reservoir formations.
Introduction
To account for reservoir heterogeneity in 3D reservoir modeling, advanced techniques are required to improve the accuracy and reliability of estimating missing core-analysis data points. The imputation of missing data refers to a range of statistical and machine-learning (ML) methods that supplement core-sample reanalysis or additional core-sample collection to fill data gaps.
This study evaluates seven data-imputation methods involving ML algorithms:
- Iterative robust model-based imputation (IRMI)
- MICE combined with CART
- Random imputation of missing data (RIMD)
- Sequential imputation (SEQimpute)
- Random forest imputation (RF)
- Principal component analysis imputation (PCA)
- Multiple imputation of incomplete multivariate data (AMELIA package)
These core-data imputation methods are applied to two wells penetrating the clastic Zubair formation of the North Rumaila oil field.