细粒运移是地层损害的主要原因;分离的粘土会迁移并损害油井产能。石油储层中会遇到两种类型的破坏性粘土:地质时期在颗粒表面生长的自生粘土,以及由于局部应力而从颗粒上脱落的碎屑粘土。整篇论文中描述的工作的目的是开发一个实验室程序来估计自生粘土对地层的损害,并推导岩心规模的数学模型。
背景
碎屑颗粒通过静电力附着在基底上,可以使用 DLVO 理论进行建模。然而,大多数岩心样本都含有一定的自生粘土含量(即与岩石结合的粘土颗粒)。为了研究自生粘土脱离造成的地层损害,应该提出一种新的公式。
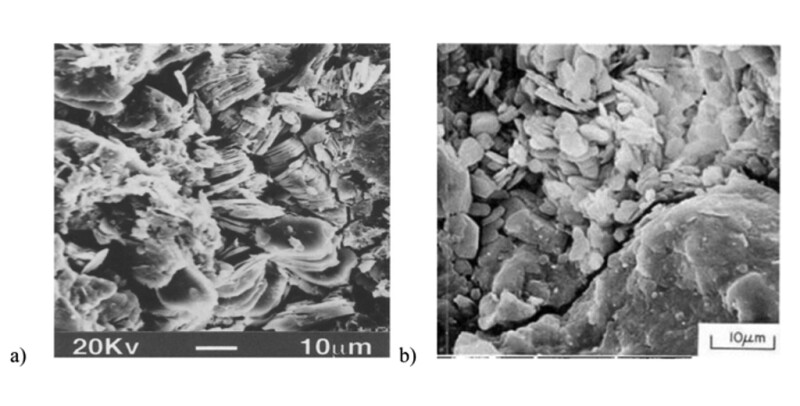
细粒运移是地层损害的主要原因;分离的粘土会迁移并损害油井产能。石油储层中会遇到两种类型的破坏性粘土:地质时期在颗粒表面生长的自生粘土,以及由于局部应力而从颗粒上脱落的碎屑粘土。整篇论文中描述的工作的目的是开发一个实验室程序来估计自生粘土对地层的损害,并推导岩心规模的数学模型。
碎屑颗粒通过静电力附着在基底上,可以使用 DLVO 理论进行建模。然而,大多数岩心样本都含有一定的自生粘土含量(即与岩石结合的粘土颗粒)。为了研究自生粘土脱离造成的地层损害,应该提出一种新的公式。

Fines migration is a major cause of formation damage; the detached clays migrate and impair well productivity. Two types of damaging clays are encountered in petroleum reservoirs: authigenic clays that grew on the grain surfaces during geological times, and detrital clays that have been broken off the grains because of local stresses. The aim of the work described in the complete paper was the development of a laboratory procedure to estimate formation damage by authigenic clays and the derivation of a mathematical model for core scale.
Detrital particles are attached to a substrate by an electrostatic force and can be modeled using the DLVO theory. Most core samples, however, have some authigenic clay content (i.e., clay particles bonded to rock). To study formation damage caused by the detachment of authigenic clay, a new formulation should be presented.
