The Hydraulic Fracturing Test Site 2 (HFTS-2) is a large collaborative field-based research and development program in the Permian Delaware Basin funded by the US Department of Energy through the National Energy Technology Laboratory and the exploration and production industry with support from academia. The project’s main objective is to improve the understanding of the hydraulic fracturing process through use of advanced diagnostics and collection of through-fracture cores to provide undisputable evidence and attributes of created fractures.
Project Background
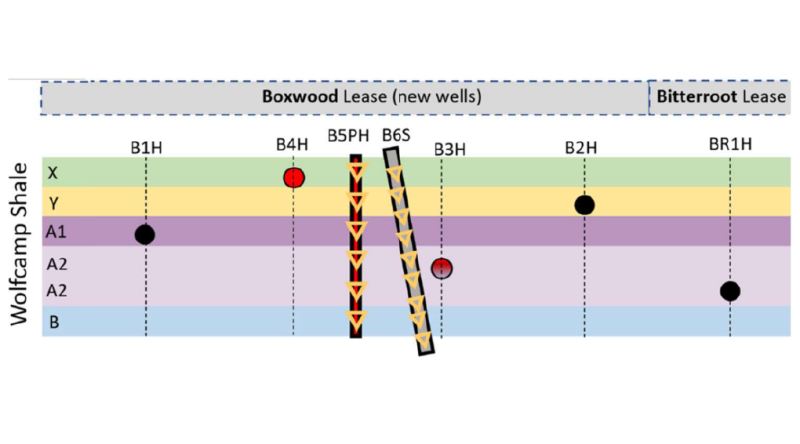
The HFTS-2 project provides the opportunity to address the optimal development of a stacked pay resource that requires simultaneous drilling and completion of tens of thousands of wells across multiple geologic horizons, also known as cube development.
The project consists of a series of coupled analytic and field experiments in which research-quality data are acquired in dedicated research wells through full instrumentation at, and in proximity to, hydraulically fractured wells. Furthermore, the unique site design provides an opportunity to understand the effect of reservoir depletion because many child-well stages overlap parent-well areas. The extensive data set acquired was integrated and used to calibrate subsurface models and characterize fracture geometry and proppant distribution.