致密气田从大型非均质河流储层中生产天然气,边缘和评价区的井控有限,且高级测井稀疏。完整论文中描述的研究的主要目标是提供一种新颖的解决方案,使用机器学习 (ML) 技术来预测砂岩分布,并在某种程度上自动化优化井位的过程。所提出的工作流程克服了数据质量低、规模大和不一致的问题,并在地球科学和人工智能 (AI) 软件平台之间架起了桥梁。
介绍
该气田是中国鄂尔多斯盆地大面积的非常规气藏。该气田从复杂且非均质的河流储层中生产天然气,砂体分布预测的井控有限。
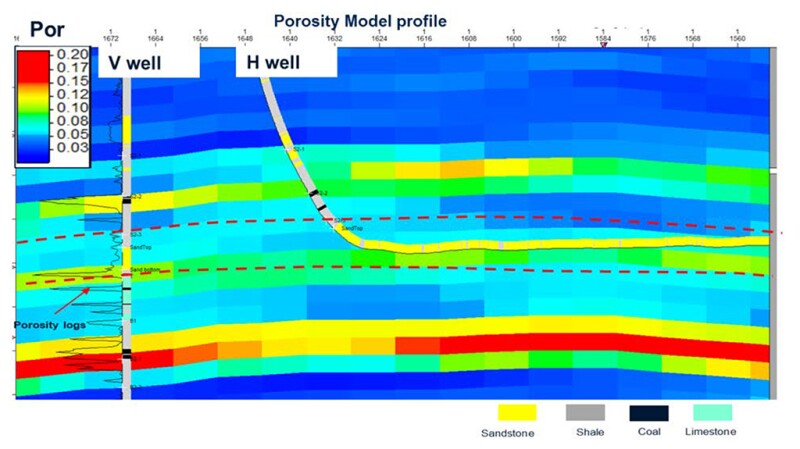
致密气田从大型非均质河流储层中生产天然气,边缘和评价区的井控有限,且高级测井稀疏。完整论文中描述的研究的主要目标是提供一种新颖的解决方案,使用机器学习 (ML) 技术来预测砂岩分布,并在某种程度上自动化优化井位的过程。所提出的工作流程克服了数据质量低、规模大和不一致的问题,并在地球科学和人工智能 (AI) 软件平台之间架起了桥梁。
该气田是中国鄂尔多斯盆地大面积的非常规气藏。该气田从复杂且非均质的河流储层中生产天然气,砂体分布预测的井控有限。

A tight gas field produces gas from a large heterogeneous fluvial reservoir with limited well control in margins and appraisal areas and sparse advanced logs. The principal goal of the study described in the complete paper was to provide a novel solution using machine-learning (ML) techniques to predict sandstone distribution and, to some extent, automate the process of optimizing well placement. The presented work flow overcomes low data quality, scaling, and inconsistency and builds the bridge between geoscience and artificial intelligence (AI) software platforms.
The field is an unconventional gas reservoir covering a vast area in the Ordos Basin in China. This field produces gas from a complex and heterogeneous fluvial reservoir with limited well control for prediction of sand-body distribution.
