The complete paper presents the results of a comprehensive study aimed at improving the understanding of deep bottom-up water injection, which enabled optimizing recovery in a heavy oil field in south Oman. The work concludes that the well-reservoir-management (WRM) strategy for a heavy oil field is not the same as one for a classic light oil waterflood. Nevertheless, the reservoir heterogeneity, oil-column thickness, and saturation history also are important factors for variable water-injection response in a heavy oil field.
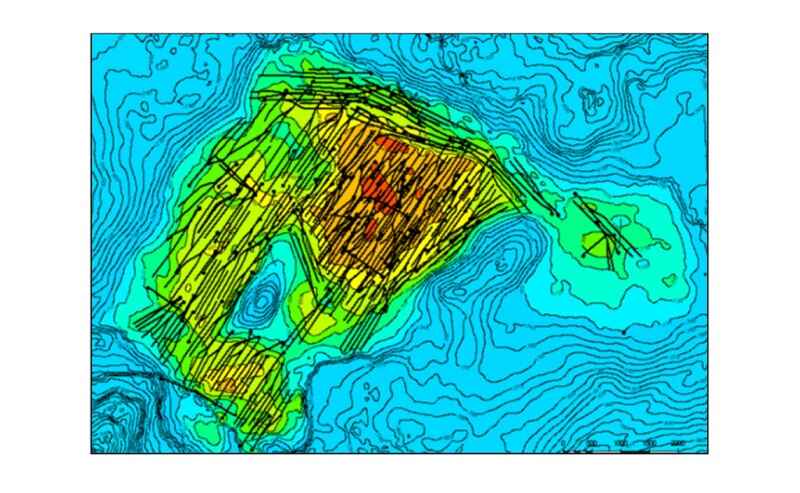
Field Background
The G field is on the eastern flank of the South Oman Salt Basin 700 km south of Muscat. The main producing reservoir, the Mahwis sand of the Haima group, culminates in two accumulations (G Main and G East). The Mahwis formation is composed of clastic sediments interlayered with several cemented zones, which often act as baffles in some areas (Fig.